A table is a database object that stores data in the form of rows and columns. The structure of a table is defined by the columns it contains.
SQL statements
DDL – Data Definition Language (CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE)
- CREATE TABLE – Creating a table
- Table name: The names of tables must be unique within the owner’s context. In other words, two tables with the same name cannot belong to the same owner, but another user may have a table with the same name.
- Column names (fields): Column names are unique within a table. Column names adhere to standard rules for choosing identifiers and consist of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Data types:
- Character (string) types:
- CHAR(n) or CHARACTER(n) – default length: 1 and max length: 255
- CHARACTER VARYING(n) or CHAR VARYING(n)
- Numeric types:
- SMALLINT, INT2, INTEGER, INT, INT4, BIGINT, INT8
- REAL, FLOAT4, DOUBLE PRECISION, FLOAT8, FLOAT
- NUMERIC(p,s), DECIMAL (p,s)
- MONEY
- Boolean and binary types: BOOLEAN, BOOL, BIT
- Date and time type: DATE, TIME, INTERVAL, DATETIME
- Data types in MS Access SQL:
- TEXT(n) – Variable-length text, maximum length of n characters
- MEMO – Text, for volume exceeding 255 characters
- BYTE, INTEGER, LONG – Integer numbers
- COUNTER – Counter, integer numbers
- SINGLE, DOUBLE, CURRENCY – Floating-point numbers
- DATETIME – Date and time
- YESNO – Logical type
- LONGBINARY – OleObject, binary type
- Character (string) types:
- Memory size
- Mandatory columns
- Primary key columns
- Foreign key columns
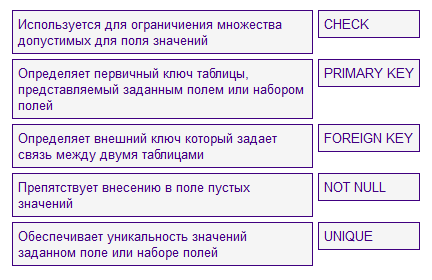
- Constraints
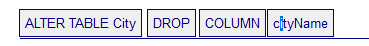
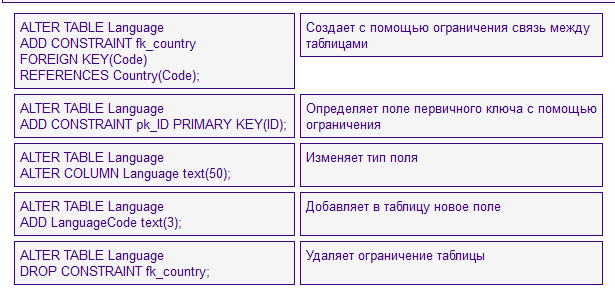
- ALTER TABLE – Modifying the structure of a table
- DROP TABLE – Deleting a table
- CREATE INDEX – Creating an index
- ALTER INDEX – Modifying an index
- DROP INDEX – Deleting an index
DML -Data Manipulation Language (INSERT INTO, DELETE FROM, UPDATE)
Table creation (DDL)
CREATE TABLE toode(
toodeID int primary key AUTO_INCREMENT,
toodeNimetus varchar(50),
toodeHind decimal(5, 2),
v_kuupaev date,
kas_olemas bit
);
Adding data to the table (DML)
INSERT INTO toode(toodeNimetus, toodeHind, kas_olemas, v_kuupaev)
VALUES ('piim Alma', 1.50, 1, '2024-01-31');
SELECT * FROM toode;
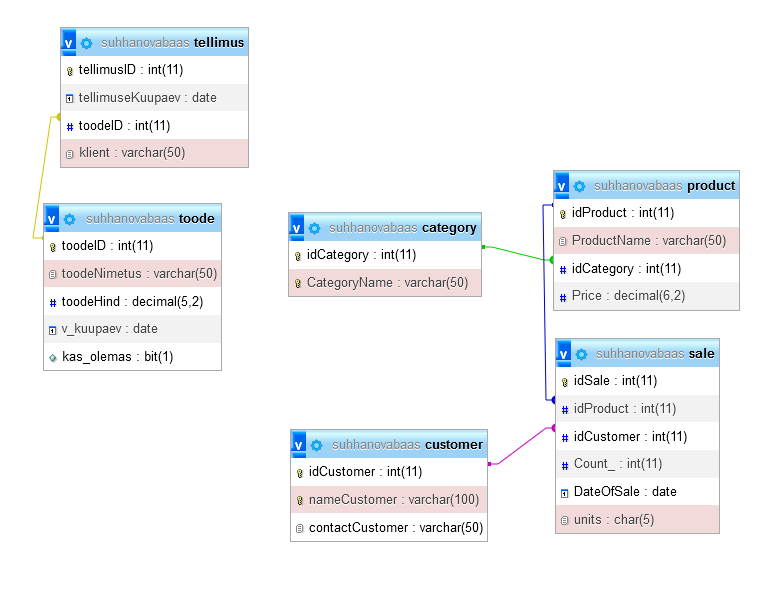
CREATE TABLE `suhhanovabaas`.`tellimus` (`tellimusID` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , `tellimuseKuupaev` DATE NOT NULL , `toodeID` INT NOT NULL , `klient` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`tellimusID`)) ENGINE = InnoDB;
Constraints – Piirangud (Ограничения)
PRIMARY KEY – The column value is unique
FORIGEIN KEY – The column uses a value from a related table.
NOT NULL – Non-empty value
UNIQUE – Unique values
CHECK – Selection of certain values
TEST



CREATE table Product(
idProduct int primary key AUTO_INCREMENT,
ProductName varchar(50),
idCategory int,
Price decimal(6, 2),
FOREIGN key(idCategory) REFERENCES category(idCategory)
);
create table customer(
idCustomer int PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
nameCustomer varchar(100) UNIQUE,
contactCustomer varchar(50)
);
insert into product(ProductName, idCategory, Price)
VALUES ('boots', 3, 100.99)
insert into Sale(idProduct, Count_, DateOfSale)
values(1,200,'2024-01-31'),(3,200,'2024-01-31'),(4,100,'2024-01-31'),(3,250,'2024-01-31'),(3,57,'2024-01-31');
insert into customer(nameCustomer, contactCustomer)
values('Marko', 55614815');
ALTER TABLE sale ADD units char(5);
alter table sale add FOREIGN KEY(idCustomer) REFERENCES customer(idCustomer)
update sale set idCustomer=1;