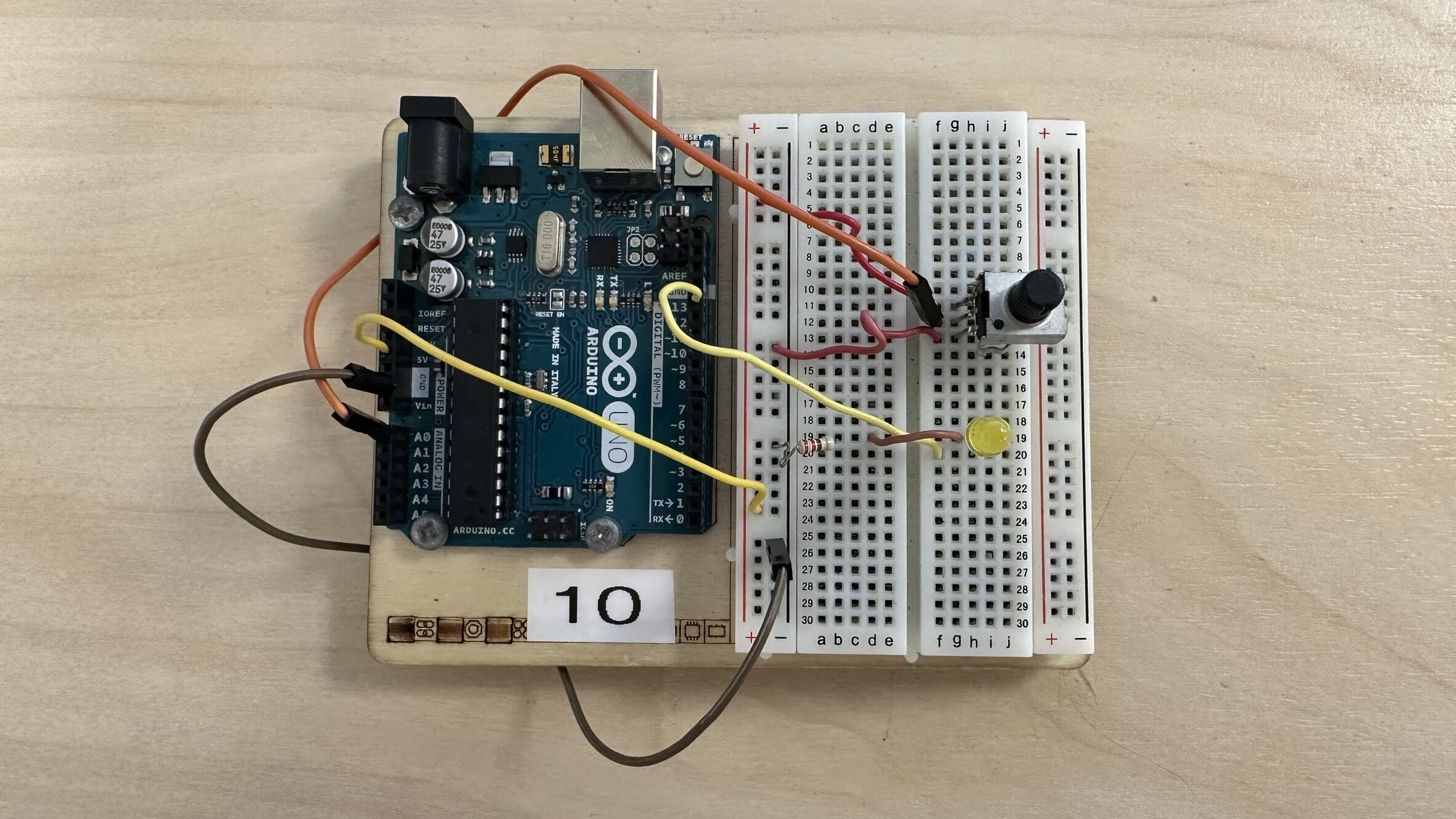
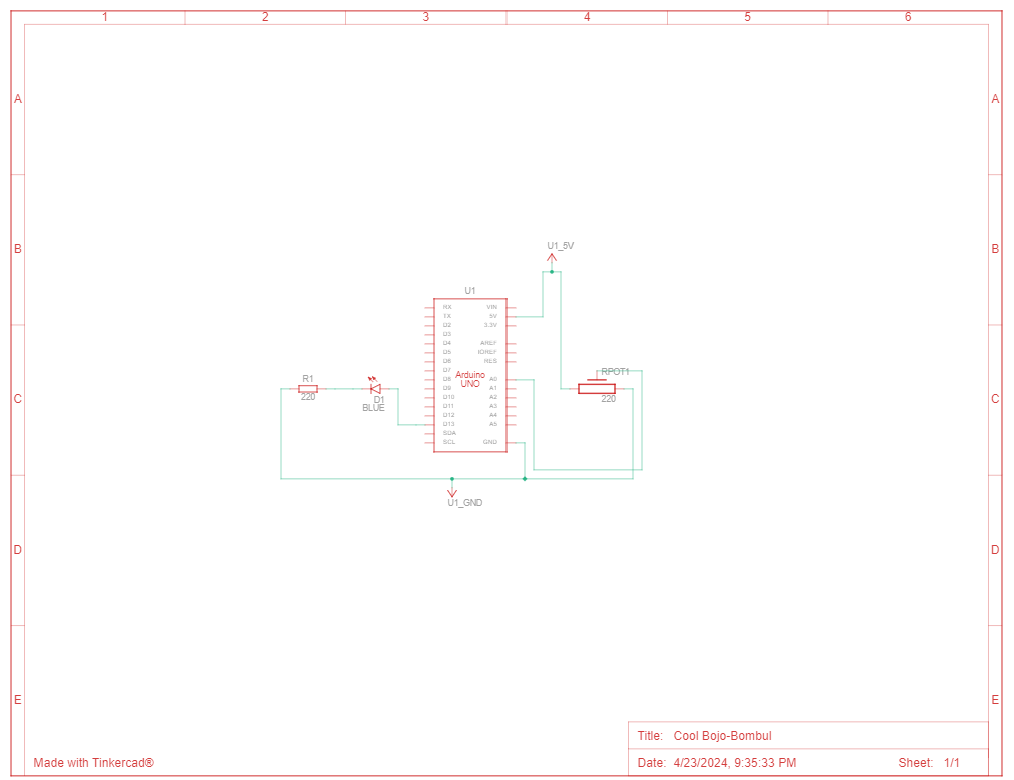
Using a potentiometer
Potentiometer is a variable resistor that allows for manual adjustment of electrical resistance, often used for controlling volume or brightness in electronic devices.
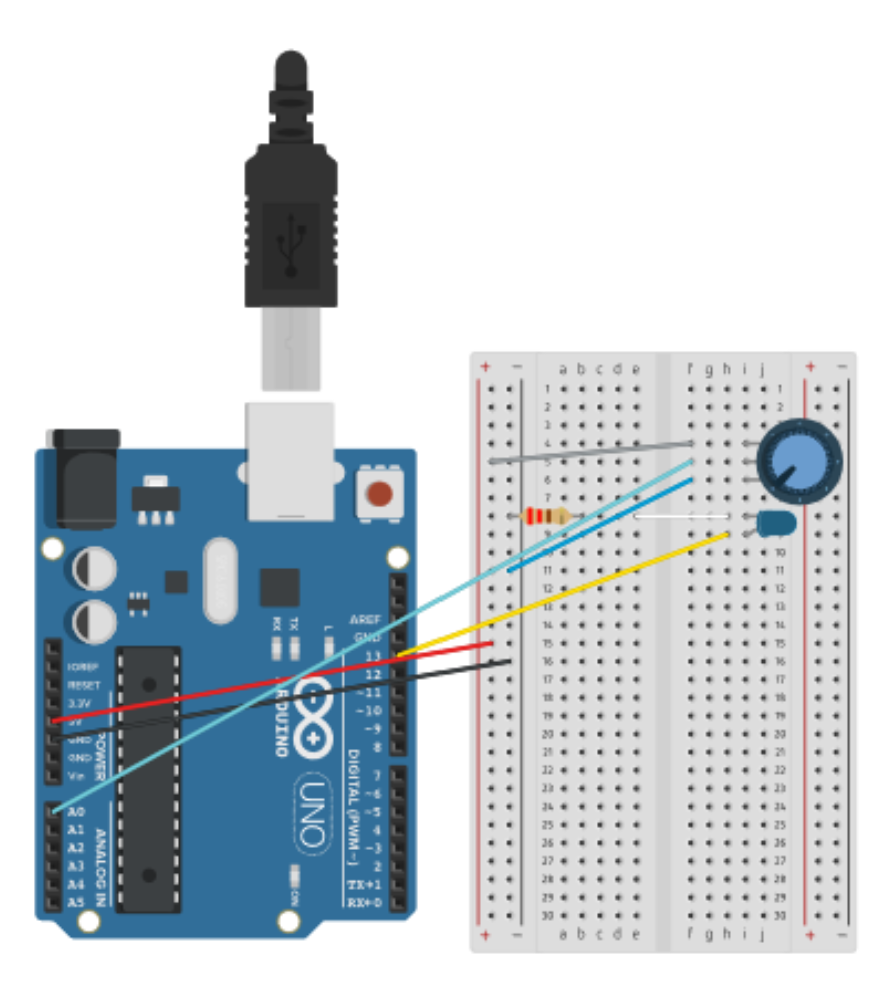
int sensorPin = 0;
int ledPin = 13;
int sensorValue = 0;
void setup()
{
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(sensorValue);
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(sensorValue);
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
Serial.println(voltage);
}

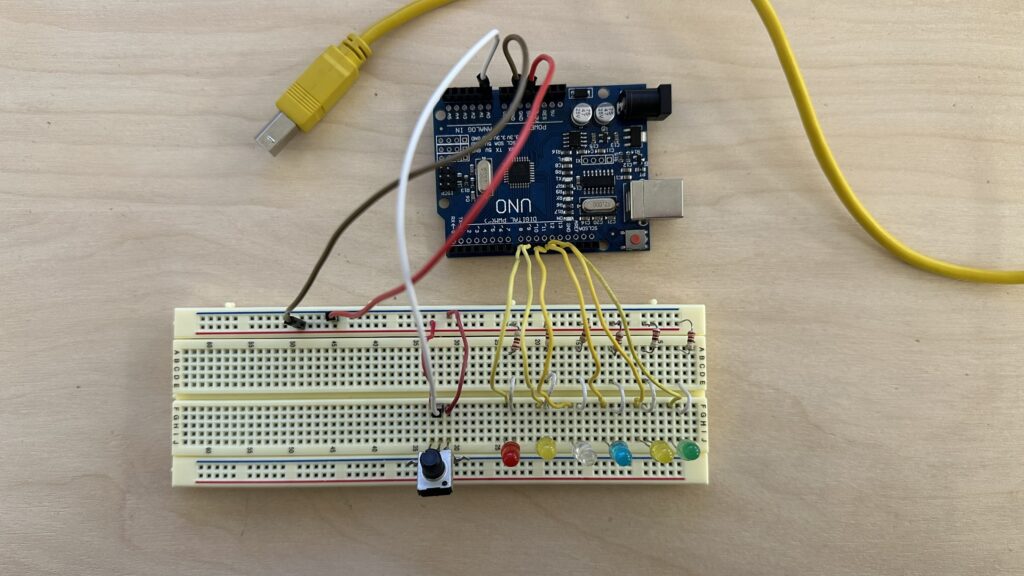
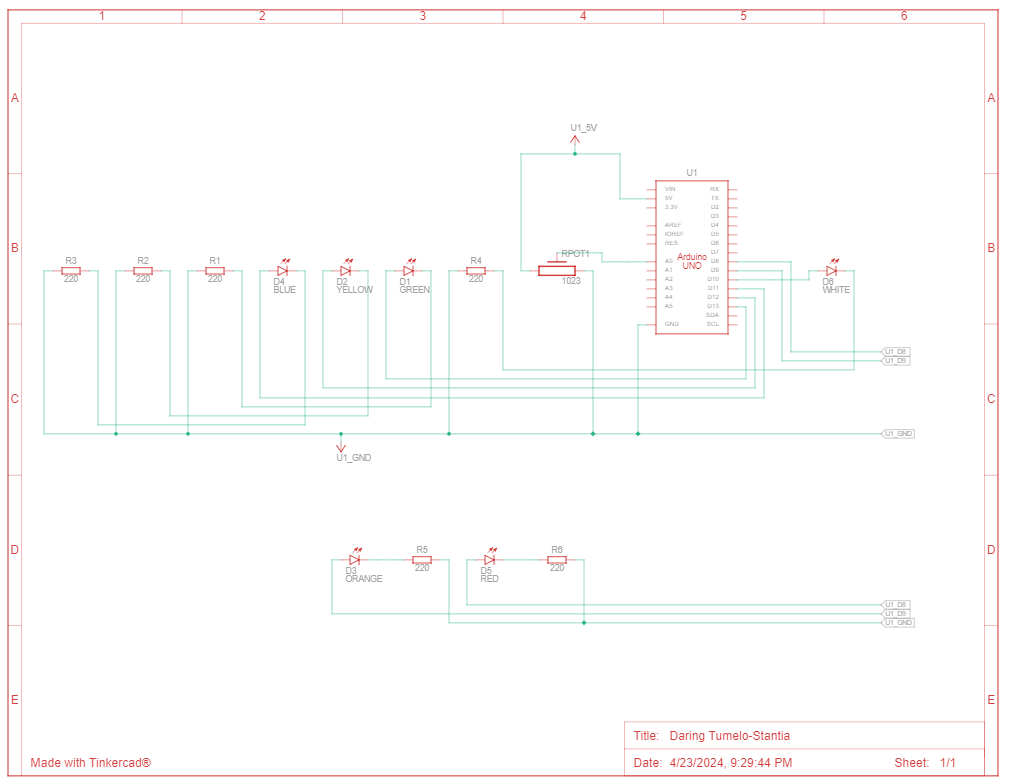
LED Garland
This Arduino code controls a series of LEDs using a potentiometer to select different lighting modes.
int ledPins[] = {13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8};
int numOfLeds = 6;
void setup()
{
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i++) {
pinMode(ledPins[i], OUTPUT);
}
}
void loop() {
int potValue = analogRead(A0);
int mode = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 1, 6);
switch (mode) {
case 1:
modeOne();
break;
case 2:
modeTwo();
break;
case 3:
modeThree();
break;
case 4:
modeFour();
break;
case 5:
modeFive();
break;
case 6:
modeSix();
break;
}
}
void turnAllOff() {
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i++) {
digitalWrite(ledPins[i], LOW);
}
}
void modeOne() {
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i++) {
turnAllOff();
digitalWrite(ledPins[i], HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(ledPins[i], LOW);
delay(500);
}
}
void modeTwo() {
turnAllOff();
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i++) {
digitalWrite(ledPins[i], HIGH);
}
delay(1000);
turnAllOff();
delay(1000);
}
void modeThree() {
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i++) {
for (int brightness = 0; brightness <= 255; brightness++) {
analogWrite(ledPins[i], brightness);
delay(10);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i++) {
for (int brightness = 255; brightness >= 0; brightness--) {
analogWrite(ledPins[i], brightness);
delay(10);
}
}
}
void modeFour() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
turnAllOff();
delay(250);
for (int j = 0; j < numOfLeds; j++) {
digitalWrite(ledPins[j], HIGH);
}
delay(250);
}
turnAllOff();
}
void modeFive() {
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i += 2) {
digitalWrite(ledPins[i], HIGH);
if (i + 1 < numOfLeds) {
digitalWrite(ledPins[i + 1], LOW);
}
}
delay(1000);
for (int i = 0; i < numOfLeds; i += 2) {
digitalWrite(ledPins[i], LOW);
if (i + 1 < numOfLeds) {
digitalWrite(ledPins[i + 1], HIGH);
}
}
delay(1000);
}
void modeSix() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int randLed = random(0, numOfLeds);
turnAllOff();
digitalWrite(ledPins[randLed], HIGH);
delay(200);
}
turnAllOff();
}
Here’s a breakdown of the code:
- Initialization:
ledPins[]: An array containing the pin numbers to which the LEDs are connected.numOfLeds: Number of LEDs connected.
- Setup Function:
- Configures each pin specified in
ledPins[]array as an output pin.
- Configures each pin specified in
- Loop Function:
- Reads the analog value from pin A0, connected to a potentiometer, and maps it to select one of six modes.
- Based on the selected mode, it calls corresponding functions.
- Mode Functions:
turnAllOff(): Turns off all LEDs.modeOne(): Sequentially lights up each LED and then turns it off with a delay.modeTwo(): Simultaneously turns on all LEDs for a brief period and then turns them off.modeThree(): Gradually increases and decreases the brightness of each LED.modeFour(): Alternates between turning all LEDs on and off in quick succession.modeFive(): Alternates between lighting up pairs of adjacent LEDs.modeSix(): Randomly selects LEDs to turn on and off in quick succession.
This code provides a versatile way to control multiple LEDs with various lighting patterns based on the input from a potentiometer